问题

海外网友Gifford Delle的回答
Almost everything in Japanese culture originates from China in some way, from Chinese characters to sushi, kimono and Buddhism; All this can be traced back to more than 2000 years ago.
日本文化中几乎所有的东西都以某种方式源自中国,从汉字到寿司、和服和佛教;这一切都可以追溯到2000多年前。
The relationship between Chinese and Japanese cultures has existed for nearly 2000 years, and the impact of this connection is still there. As the older and more mature of the two civilizations, Chinese culture has had a huge impact on almost all aspects of Japanese life. You can see the influence of Chinese culture on Japanese culture in many ways.
中日文化之间的关系已经存在了近2000年,这种联系的影响至今仍在。作为两种文明中更古老和成熟的一方,中国文化几乎对日本生活的各个方面都产生了巨大影响。你可以从很多方面看到中国文化对日本文化的影响。
语言/language
When the two civilizations first met, the Japanese characters had not yet taken shape. Therefore, when the two cultures met, the Japanese adopted Chinese characters, which made the exchange between empires possible. Over the centuries, the writing styles of these two cultures have undergone great changes, so that they are now unique.
当两个文明首次相遇时,日语文字还没有成形。因此,当两种文化相遇时,日本人采用了汉字,从而使帝国之间的交流成为可能。几个世纪以来,这两种文化的写作风格都发生了很大的变化,以至于现在都是独一无二的。
宗教/religion
Because Japan does not have its own organized religion, when the two cultures meet, Buddhism and Confucianism form a strong attraction to Japan. Although many people in Japan still follow their ancient Shinto faith, there are still a large number of Buddhist believers in Japan today. Even in the local Shinto practice, the art of building permanent shrines and temples also comes from Chinese Buddhism.
由于日本没有自己的有组织的宗教,当两种文化相遇时,佛教和儒家对日本形成了强烈的吸引力。尽管日本的许多人仍然遵循他们古老的神道教信仰,但今天仍有大量佛教信徒在日本。即使在本土的神道教实践中,建造永久神社和寺庙的艺术也来自于中国的佛教。
官僚系统/Bureaucratic system
Although both countries had imperial government in the past, the Mikado of Japan adopted many advantages of the Chinese bureaucracy, including various titles, grades and official functions. The first form of their constitution was influenced by the more centralized and organized government in ancient China.
尽管两国过去都有朝廷形式的政府,但日本天皇采纳了中国官僚体系的许多优点,包括各种头衔、等级和官方职能。他们宪法的第一种形式受到了中国古代政府更加集权和组织化的影响。
建筑学/architecture
With the introduction of Buddhism into Japan, the practice of building exquisite temples also rose. With this development, other buildings began to adopt more complex forms, including larger rooms and internal courtyards. The classic arc roof style is definitely influenced by China and can still be seen in all parts of Japan today.
随着佛教传入日本,建造精致寺庙的做法也随之兴起。随着这一发展,其他建筑开始采用更复杂的形式,包括更大的房间和内部庭院。经典的弧形屋顶风格肯定来自中国的影响,今天在日本各地仍然可见。
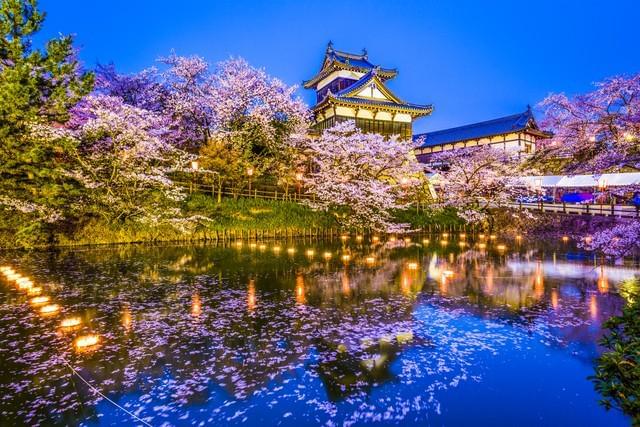

城市规划/city planning
The urban planning method in ancient China involves organizing urban roads into regular rectangles for navigation and communication. You can see that this concept has been applied in Japanese cities such as Kyoto and Nara. Even farmland and irrigation systems have begun to use this organized and efficient system.
中国古代的城市规划方法涉及将城市道路组织成规则的矩形,以便于导航和沟通,你可以看到这一概念在日本城市如京都和奈良得到了应用。即使是农田和灌溉系统也开始使用这种有组织和高效的系统。
艺术/Art
With the introduction of Buddhist monks and temples, a new artistic style emerged at the historic moment. The entire art world in Japan has incorporated many Chinese elements in various times. Painting and sculpture were developed to show Buddhist concepts, which affected the whole artistic scene. During the Nara period, it was very popular to paint on exquisite paper with Chinese ink, including many forms of decorative scrolls. The practice of calligraphy as an art medium also came to Japan.
随着佛教僧侣和寺庙的传入,新的艺术风格应运而生,日本的整个艺术世界在各个时代都融入了许多中国元素。绘画和雕塑是为了展示佛教观念而发展起来的,这影响了整个艺术场景。在奈良时期,用中国墨水在精美的纸上作画非常流行,包括许多形式的装饰卷轴。书法作为一种艺术媒介的实践也来到了日本。
Other forms of art, including the masked opera called Gigaku, come from China, and so do the Gagaku court dance.
其他形式的艺术,包括被称为Gigaku的蒙面剧,来自中国,Gagaku宫廷舞蹈也是如此。
音乐/Music
The music world is deeply influenced by China, partly because of the introduction of new music styles, but also by the influence of new musical instruments. As part of Buddhist rituals, different forms of bells, gongs and jingles were introduced into Japan, and these new sounds soon became popular music at that time. This is most obvious in kabuki music style.
音乐世界深受中国的影响,部分原因是引入了新的音乐风格,但也受到了新乐器的影响。作为佛教仪式的一部分,不同形式的钟、锣和响叮当声传入日本,这些新的声音很快成为当时流行的音乐。这在歌舞伎音乐风格中最为明显。
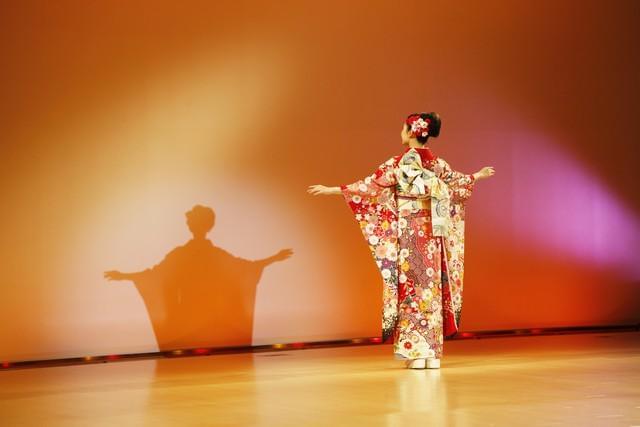

服装/Clothing
Although kimono seems to be a typical Japanese costume, its inspiration comes from China in the Han Dynasty. Ironically, the clothing styles of both countries have been further influenced by western styles, so that traditional clothing is becoming more and more uncommon.
虽然和服似乎是典型的日本服装,但它的灵感来源于汉代的中国。具有讽刺意味的是,这两个国家的服装风格都受到了西方风格的进一步影响,以至于传统服装越来越不常见。
So we can say that Japanese culture does not come from China. On the contrary, Chinese culture reshaped Japanese culture in ancient times. Japanese culture exuded a strong Chinese flavor, and then formed the prototype of modern Japanese culture.
所以我们可以说,日本文化并非来自中国。相反,中国文化在古代重塑了日本文化,日本文化散发着浓郁的中国香味,然后形成了现代日本文化的原型。
日本网友Mona Yunita的回答
I am not a historian or an expert in East Asian history. So my answer may be a little inaccurate. The most appropriate answer to this question is "Chinese centralism".
我不是历史学家或东亚历史专家。所以我的回答可能有点不准确。这个问题最合适的答案是“中国中心主义”。
For thousands of years, Chinese people have always regarded themselves as the center of the world, the cradle of civilization and the country of culture. They believe that people living outside their own fields are barbaric, barbaric, uncivilized and uneducated.
几千年来,中国人一直认为自己是世界的中心、文明的摇篮、文化的国度。他们认为生活在自己领域之外的人是野蛮、野蛮、未开化和未受教育的。
The Chinese have indeed invented many ingenious inventions. They also discovered many scientific phenomena, some of which were not known to the western world until the Renaissance and the Enlightenment. However, the Chinese people at that time did not know that their China-centric ideology was slowly engulfing them from inside.
中国人确实发明了许多巧妙的发明。他们还发现了许多科学现象,其中一些直到文艺复兴和启蒙时代才为西方世界所知。然而,当时的中国人并不知道他们的中国中心主义思想正在从内部慢慢吞噬他们。
In the Han, Tang, Song and Ming dynasties, Chinese civilization reached the golden age. As China is the most powerful country in the region, its culture will naturally be exported to other countries with close relations with China. We can see the same thing happening today. American culture has influenced and shaped a friendly country. South Korea and the Philippines are typical examples.
在汉、唐、宋、明三代,中国文明达到了黄金时代。由于中国是该地区最强大的国家,其文化自然会被输出到与中国关系密切的其他国家。我们今天可以看到同样的事情发生。美国文化影响并塑造了对她友好的国家。韩国和菲律宾就是典型的例子。
It is not uncommon for Japanese to adapt to foreign culture (or any good culture). In fact, this seems to be the essence of Japanese society. But we must remember that, unlike many other countries, the Japanese not only adapt, but also improve and modify the elements that are beneficial to them.
对日本人来说,适应外国文化(或任何好的文化)并不罕见。事实上,这似乎是日本社会的本质。但我们必须记住的一点是,与许多其他国家不同,日本人不仅适应,而且还改进和修改对他们有益的元素。
Take garden architecture as an example. Chinese gardens were introduced to Japan in the 11th century. The Japanese not only adapted to this, but also modified the concept and added some local elements to it. The final result is a Zen garden - a miniature garden that mimics the nature of nature. Imitating the nature or capturing the beauty of nature is the core concept of Chinese garden. So we can see here that the Japanese have built a better or unique garden on the basis of Chinese elements.
以花园建筑为例。中国式花园大约在11世纪传入日本。日本人不仅适应了这一点,还修改了这一概念,并在其中加入了一些本地元素。最终的结果是禅宗花园——一个模仿自然本质的微型花园。模仿自然的本质或捕捉自然的美是中国式园林的核心理念。所以我们可以在这里看到,日本人在中国元素的基础上建造了一个更好或独特的花园。

不仅仅是园林建筑、纸艺(包括折纸或折纸)、食品等都被进口到日本,日本人最终使这些变得更好。折纸是另一个很好的例子。折纸艺术最早是由纸的发明者中国人发明的。但中国人只在为死者制作简单的纸制品时使用了这种艺术。然而,当这种艺术被引进日本时,他们发展并发扬了它,使这种曾经简单的艺术变成了一种复杂而迷人的折纸艺术。正是日本人把这种精致的艺术做得更好,全球闻名。

折纸艺术
What do I mean? In my opinion, Japan has indeed borrowed many elements from Chinese culture. Many seemingly unique Japanese elements originate from China. However, many Chinese are unwilling to admit that the Japanese are doing better than them. This is like the fable of grapes and foxes. The Chinese can't achieve the achievements of the Japanese, but they soon infer that the Japanese are not as good as the Chinese, and their achievements are only the shadow of China's greatness. This mentality is the main reason why many Chinese believe that everything comes from China.
我的意思是什么?我的观点是,日本确实从中国文化中借鉴了很多元素。许多看起来独特的日本元素都源自中国。但是,许多中国人不愿承认日本人做得比他们好。这就像葡萄和狐狸的寓言,中国人无法实现日本人所取得的成就,但他们很快就推断出日本人不如中国人,他们的成就只是中国伟大的影子。这种心态是许多中国人认为一切都来自中国的主要原因。

日本网友To run Shimojima的回答
Because this is partly correct. Just like when the United States is the most powerful country in the world, many students will study abroad and study American history, civil structure, history, technology, natural language, and some cultures, such as music and movies, in the United States. This is very similar to how Britain's food, language, football, fashion taste and food spread around the world when Britain was the strongest country, or how France became the popular upper-class noble language and dominated the European fashion industry when France was the strongest country.
因为这是部分正确的。就像当美国是世界上最强大的国家时,许多学生会出国留学,在美国学习美国的历史、公民结构、历史、技术、自然语言,以及一些文化,如音乐、电影。这与英国是最强的国家时,英国的食物、语言、足球、时尚品味、食物如何在世界各地传播,或者法国是最强国家期间,如何成为流行的上层贵族语言,并在欧洲时尚界占据主导地位非常相似。
In ancient times, China was the most dominant and advanced country in the Far East. Therefore, this is very common to Japan, which is unique, but it must be because its advance personnel came to China to study. If you look back on the relationship between the Tang Dynasty and Japan, there is a special person, the Tang envoy, Kent ō Sh, this is a special status for smart Japanese missionaries, who came to the Tang Dynasty with efforts to learn Chinese culture and civilization.
在古代,中国是远东地区最具统治力和最先进的国家。因此,这对日本来说是很常见的,这是独特的,但肯定是因为它的先遣人员到中国学习,如果你回顾唐朝和日本的关系,有一个特殊的人,遣唐使, Kentōsh,这是给聪明的日本传教士的特殊地位,带着学习中国文化和文明的努力来到了唐朝。
If you look at some traditional Japanese arts, crafts, fabrics and makeup, you will find many things similar to ancient Chinese art. In a sense, the Japanese also learned from the writing system of China and the civil system and built it into their own writing system. Unifying the nation is more effective than unifying the language. Mountains and rivers often cause division, leading people to develop different dialects and customs. Once different writing develops, it will eventually lead to different cultural identity, and the common writing system allows systematic teaching and unifies the fragmented territory.
如果你看看日本的一些传统艺术、工艺、布料、化妆,你会发现很多与中国古代艺术相似的东西。从某种意义上讲,日本人也借鉴了中国和民事体系的书写体系,并将其打造成自己的书写体系,统一民族比统一语言更有效。高山大河经常造成分裂,导致人们发展出不同的方言、风俗习惯,一旦不同的书写发展起来,最终导致不同的文化认同,而共同的书写系统允许系统的教学,并将碎片领土统一在一起。
This cultural borrowing/learning continues in the world. If you look at the Japanese system after Meiji, it will become more influential in the West, although it also has its own identity.
这种文化借用/学习在世界上仍在继续,如果你看看明治之后的日本制度,它会变得更具西方影响因素,尽管它也有自己的身份。
Chinese people can also say that after the fall of the Qing Dynasty, the Republic of China adopted Chinese tunics, or woolen clothing, which is absolutely unique, but it is so different from traditional Chinese clothing and very similar to western clothing. You can be sure that the concept of suits comes from the West.
中国人也可以这样说,在清朝倒台后,民国采用了中山装,或毛装,这绝对是独一无二的,但它与传统的中国服装是如此的不同,与西方服装非常相似,你可以肯定地说,西装的理念来自西方。

日本网友Nodashi的回答
If you are affected by three factors like Chinese people, it is easy to understand.
如果你像中国人一样受到三个因素的影响,这很容易理解。
The first is ancient legends, because people do not always believe in facts, but believe in their own judgments, which may be distorted by others. Some stories, especially unofficial history, are widely spread. For example, in the Qin Dynasty, Emperor Qin Shihuang sent 3000 boys and girls to a remote island, which is said to be Japan, in search of a kind of herb that can make mankind immortal. These stories may not be true, but they have been passed down from generation to generation in books or media. If someone grows up listening to this story, he or she will have the impression that the Japanese and their culture are rooted in China.
第一种是古代传说,因为人们并不总是相信事实,而是相信自己的判断,而这种判断可能会被他人扭曲。一些故事,特别是非官方历史流传甚广。比如在秦朝时期,秦始皇派遣了三千名童男童女到一个遥远的岛屿,据说那里就是日本,寻找一种使人类不朽的药草。这些故事可能不是真的,但已经在书中或媒体上被一代又一代地传承下来。如果有人在听这个故事长大,他或她会有这样的印象:日本人和他们的文化的根在我们中国。
The second factor is the historical record. The Japanese came to China and learned social system and culture during the prosperous Tang Dynasty. More importantly, these are written in the textbooks of middle schools. So every Chinese in the compulsory education stage of middle schools knows that some Japanese came to study to improve their homeland long ago. Through a point of view, Japanese architecture, painting and books, as well as the time of building construction, painting and book writing, all conform to historical theory. However, to be fair, historical records cannot prove that Japanese culture actually comes from China, and sometimes it is misled by the judgments of the people mentioned above.
第二个因素是历史记录,日本人在盛唐时期来到中国并学习了社会制度、文化等。更重要的是,这些都写在中学课本上,所以每一个中国人在中学义务教育阶段,他们就知道很久以前,一些日本人为了改善自己的家园而来学习。通过一点,日本的建筑、绘画和书籍以及建筑建造、绘画和写书的时间都符合历史理论。然而,公平地说,历史记录并不能证明日本文化实际上来自中国,有时会被前面提到的人们的判断所误导。
Finally, every Chinese has a sense of national pride. It is common in any other country or within any other ethnic group, but it will take some time to understand. Because China has such a rich culture, especially thousands of years ago, we Chinese people are very proud of it. If other cultures have some similarities, it may come from us. It's no big deal, just makes us feel good. This kind of good feeling makes Chinese people feel proud again.
最后,每个中国人都有民族自豪感。在任何其他国家或任何其他民族内部都很常见,但需要一段时间才能理解。由于中国拥有如此丰富的文化,特别是在几千年前,我们中国人对它感到非常自豪,如果其他文化有一些相似之处,它可能来自我们,没什么大不了的,只是让我们感觉良好。这种良好的感觉再次让中国人感到自豪。

